The other day, I was chatting with a friend about his new diet plan. He was really excited about all the changes he was making and how much better he felt. But, as he talked about cutting out all carbs, I couldn’t help but think about how his blood sugar might be affected. It reminded me of a recent medical study I read about the link between lifestyle factors and blood glucose stability. This got me thinking about the importance of understanding the risks associated with unstable blood glucose levels and how we can manage them through lifestyle changes.
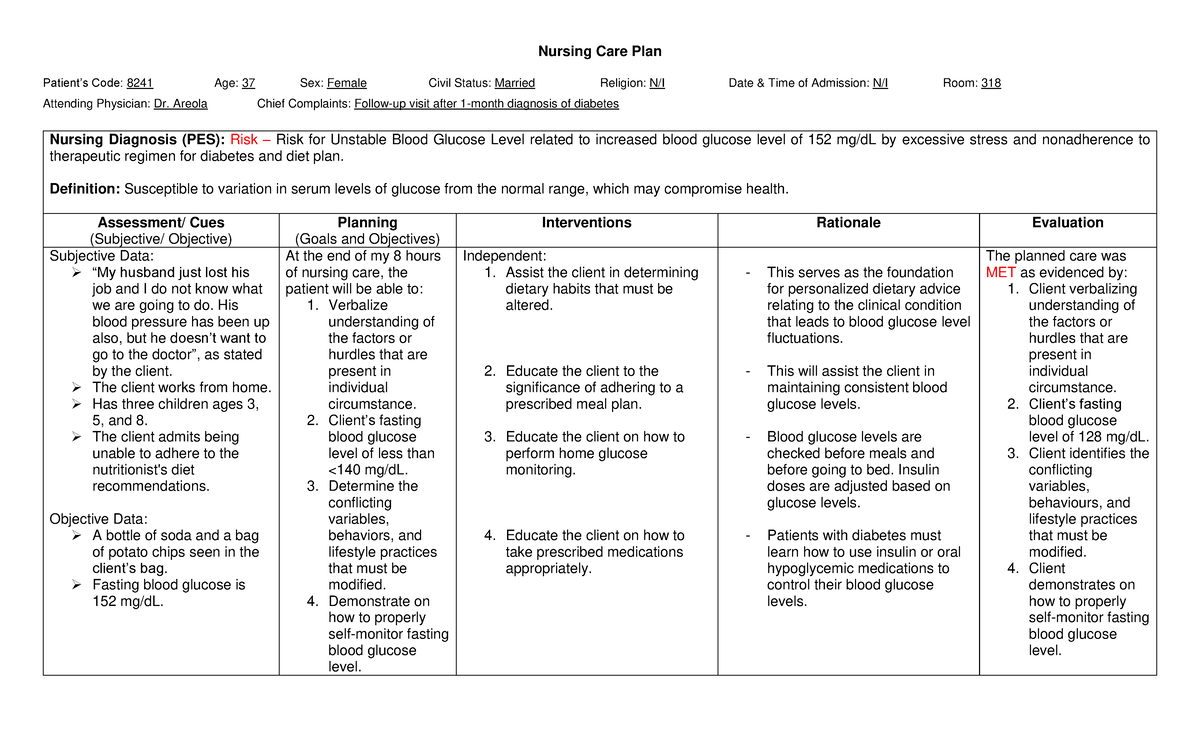
Image: www.studocu.com
Unstable blood glucose, or blood sugar, levels can lead to a range of health problems, from fatigue and weight gain to long-term complications like heart disease, stroke, and even blindness. While genetics play a role, many factors within our control can contribute to these fluctuations. From the food we eat to our stress levels, these lifestyle factors can significantly impact our blood sugar.
Understanding Blood Glucose Stability
What is Blood Glucose?
Blood glucose, also known as blood sugar, is a type of sugar that your body uses as its main source of energy. It comes from the foods you eat, primarily carbohydrates. When you eat, your body breaks down the carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into your bloodstream.
How Does Blood Glucose Regulation Work?
Your body has a complex system for regulating blood glucose levels. When your blood sugar rises after a meal, your pancreas releases a hormone called insulin. Insulin helps your cells absorb glucose from the bloodstream, lowering blood sugar levels. When your blood sugar drops, typically between meals, your pancreas releases another hormone called glucagon, which signals the liver to release stored glucose back into the bloodstream, preventing your blood sugar from dropping too low.

Image: radiointegracionboliviana.com
What is Unstable Blood Glucose?
Unstable blood glucose refers to fluctuations in blood sugar levels. While some fluctuations are normal, consistently high or low blood sugar levels can indicate a problem with your body’s ability to regulate blood glucose. This can happen because of a variety of factors such as:
- Insulin resistance: When the cells in your body don’t respond properly to insulin, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar.
- Pancreatic dysfunction: The pancreas may not be producing enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels effectively.
- Hormonal imbalances: Hormones like cortisol and growth hormone can impact blood sugar levels.
- Medications: Certain medications, like steroids, can elevate blood sugar levels.
- Lifestyle factors: These include factors such as diet, physical activity, stress levels, and sleep quality.
The Importance of Stable Blood Glucose Levels
Maintaining stable blood glucose levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. When your blood glucose is consistently high, it can damage blood vessels, leading to a higher risk of heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. High blood sugar can also contribute to nerve damage and vision problems.
On the other hand, consistently low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) can cause dizziness, confusion, and even loss of consciousness. Severe hypoglycemia can be dangerous and requires immediate medical attention. Maintaining stable blood glucose levels helps prevent both high and low blood sugar levels, thus mitigating the associated health risks.
Lifestyle Factors that Contribute to Unstable Blood Glucose
Diet
Your diet plays a significant role in blood glucose stability. Consuming foods high in processed carbohydrates, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar. These spikes can overwork your pancreas, leading to insulin resistance and increased risk for unstable blood glucose. Conversely, a balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and healthy fats helps control blood sugar levels.
Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is essential for blood glucose management. Exercise helps your cells use glucose more effectively, lowering blood sugar levels. Furthermore, exercise can improve your body’s sensitivity to insulin, making it easier to regulate blood sugar.
Stress
Chronic stress can also contribute to unstable blood glucose. When you’re stressed, your body releases hormones like cortisol, which can increase blood sugar. Managing stress through techniques like meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can help minimize the impact of stress on blood sugar levels.
Sleep
Adequate sleep is crucial for blood glucose regulation. Insufficient sleep can disrupt your body’s hormonal balance, leading to increased insulin resistance and higher blood sugar levels. Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night to maintain healthy blood sugar control.
Other Factors
Other lifestyle factors that can impact blood glucose stability include smoking, alcohol consumption, and certain medications.
Tips and Expert Advice for Managing Blood Glucose
Focus on a Healthy Diet
Choose whole grains over refined grains, focus on lean protein sources, and incorporate plenty of fruits and vegetables into your diet. Limit sugary drinks and processed foods, and be mindful of portion sizes.
Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. This can include brisk walking, jogging, swimming, biking, or dancing.
Manage Stress Levels
Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga. Find healthy ways to cope with stress, such as spending time in nature, listening to music, or engaging in hobbies.
Prioritize Sleep
Set a regular sleep schedule and create a relaxing bedtime routine. Avoid caffeine and alcohol before bed, and ensure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool.
Consult a Healthcare Professional
Talk to your doctor or a registered dietitian for personalized advice on managing blood glucose levels based on your specific needs and medical history.
FAQ
Q: What are the symptoms of unstable blood glucose?
A: Symptoms of high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) can include increased thirst, frequent urination, excessive hunger, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow-healing sores. Symptoms of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) can include dizziness, confusion, sweating, trembling, headache, and a rapid heartbeat.
Q: Can I test my blood sugar at home?
A: Yes, you can monitor your blood sugar at home using a glucometer. Your doctor can provide instructions on how to use the device and interpret the results.
Q: What are some foods that are good for blood sugar control?
A: Foods rich in fiber, like whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes, are good for blood sugar control. Lean proteins and healthy fats, like those found in nuts and seeds, also help regulate blood sugar levels.
Q: Is there anything I can do to prevent unstable blood glucose?
A: While not everyone can prevent blood glucose fluctuations, adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce your risk. This includes eating a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress levels, and getting enough sleep.
Q: When should I see a doctor about blood sugar issues?
A: If you experience any concerning symptoms related to blood sugar, such as frequent urination, excessive thirst, or unexplained weight loss, it’s essential to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Risk For Unstable Blood Glucose Related To
Conclusion
Unstable blood glucose can present a significant health risk, but understanding the lifestyle factors that influence blood sugar stability can empower you to take control of your health. By prioritizing a healthy diet, regular exercise, stress management, and sufficient sleep, you can significantly improve blood glucose regulation and reduce your risk of future complications. Remember to consult a healthcare professional if you have any concerns or questions about your blood sugar levels.
Are you interested in learning more about managing blood glucose levels or adopting a healthier lifestyle? Let me know in the comments below.






