In the ever-expanding realm of networking, IPv4 remains a cornerstone technology, responsible for connecting devices globally. As networks grow, so does the need for efficient management, and subnetting emerges as a crucial tool for organizing and controlling IP address allocation. But understanding and implementing subnetting can seem daunting, especially for those new to networking. This is where Packet Tracer, a powerful simulation tool, steps in, allowing you to experiment with subnetting concepts in a safe and interactive environment.
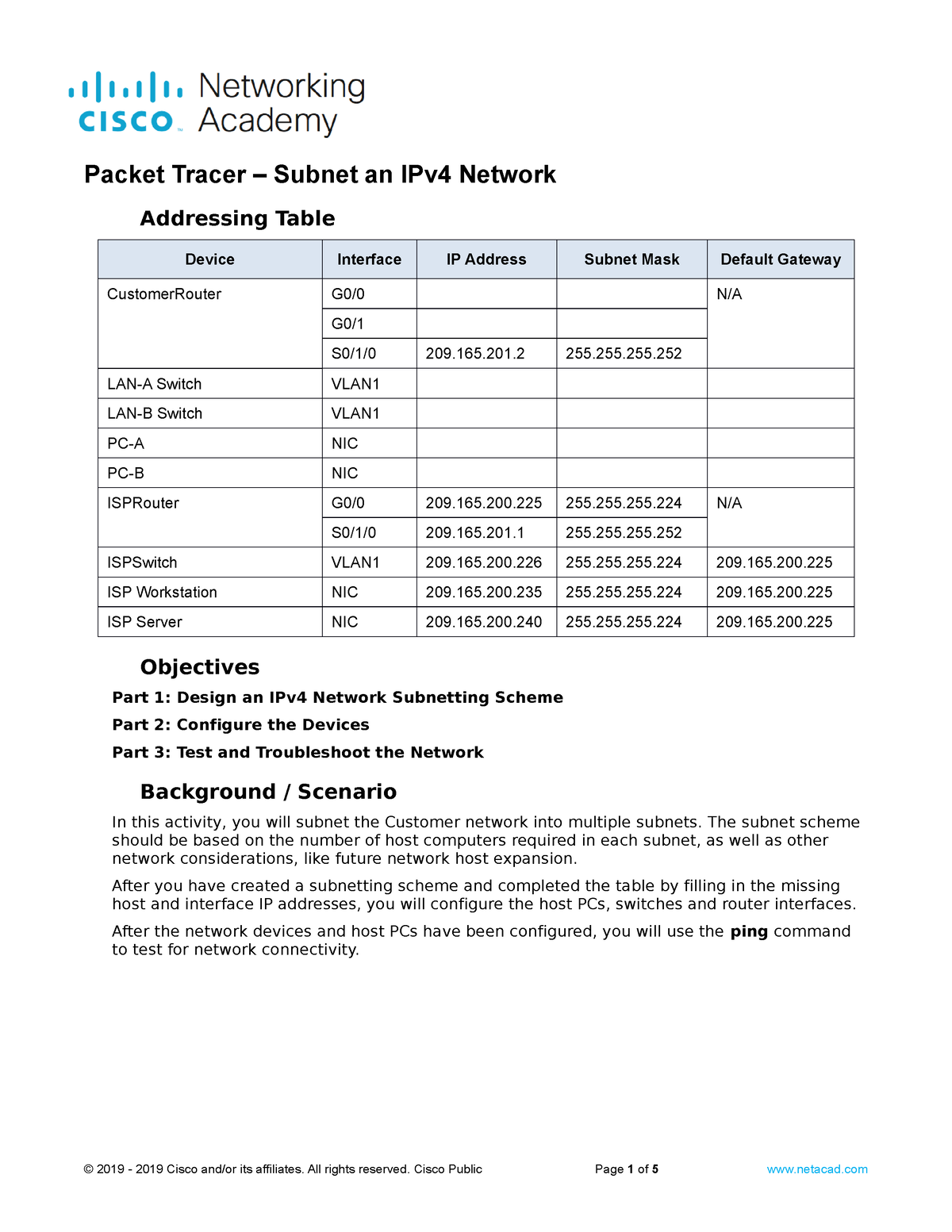
Image: www.studocu.com
In this article, we’ll embark on a journey to demystify subnetting and explore how Packet Tracer facilitates this vital process. We’ll delve into the fundamentals of subnetting, dissect its practical applications, and guide you through step-by-step procedures using Packet Tracer. Whether you’re a networking novice or a seasoned professional, this article will equip you with the knowledge and skills to confidently subnet your IPv4 networks.
Understanding Subnetting
Subnetting is essentially the division of a larger network into smaller, more manageable subnetworks. This partitioning process enables efficient IP address allocation, enhanced security, and improved network performance. Each subnetwork is identified by a unique subnet mask, which dictates how many bits are reserved for the network portion and how many are available for host addresses.
Imagine a large office building with numerous departments. Subnetting is like dividing the building into separate floors, each designated for a specific department. This compartmentalization simplifies network management, allows for tailored security policies, and improves communication efficiency within each department.
The Importance of Subnetting
Subnetting’s value lies in its multifaceted benefits, offering solutions to various network challenges:
1. Efficient IP Address Management:
Subnetting ensures that IP addresses are used judiciously, avoiding address exhaustion, especially in large networks. By dividing the network into smaller segments, you can allocate IP addresses optimally, ensuring that each subnetwork has enough addresses for its devices while reserving some for future growth.

Image: es.scribd.com
2. Enhanced Security:
Subnetting forms a natural boundary between different parts of your network. By segmenting your network, you can restrict traffic flow, preventing unauthorized access and enhancing overall security. For instance, you could create separate subnetworks for critical servers and sensitive data, limiting access to these resources to authorized personnel.
3. Improved Network Performance:
Subnetting reduces network traffic by confining communication within specific subnetworks. This isolation minimizes broadcast traffic and optimizes network performance, leading to faster data transmission and reduced latency.
4. Simplified Network Troubleshooting:
When a problem arises in a network, subnetting helps pinpoint the affected area. By isolating the subnetwork with the issue, you can efficiently identify the root cause and resolve it quickly.
Subnetting with Packet Tracer
Packet Tracer offers a simulated environment that mirrors real-world networking scenarios. This allows you to practice subnetting concepts without impacting live networks. Within Packet Tracer, you can design virtual networks, configure devices, and experiment with routing, all within a secure and flexible setting.
To subnet an IPv4 network in Packet Tracer, you’ll follow these steps:
1. Create a Network Topology:
Begin by constructing your network topology using virtual devices like routers, switches, and end devices. This step involves connecting these devices according to your desired network design, mirroring a real-world setup.
2. Configure IP Addressing:
Next, assign IP addresses and subnet masks to your devices. This involves specifying the network address, subnet mask, and available host addresses for each subnetwork. Packet Tracer provides a user-friendly interface for entering these details.
3. Configure Routing:
If your network involves multiple subnetworks, you’ll need to configure routing to enable communication between them. This typically involves setting up static routes or dynamic routing protocols on your routers to ensure seamless data transfer across different subnetworks.
4. Test Network Connectivity:
Once you’ve completed the configuration, perform tests to verify network connectivity between devices in different subnetworks. This involves sending pings, tracing routes, or accessing services across subnetwork boundaries to confirm proper communication and routing.
Tips and Expert Advice
Here are some practical tips from experienced network professionals:
1. Start Small:
When practicing subnetting, begin with a simpler network and gradually increase the complexity as you gain confidence. This allows you to master the fundamentals before tackling larger, more intricate networks.
2. Document your Configuration:
Always document your IP addressing and subnetting configurations. This documentation becomes invaluable when troubleshooting, making modifications, or expanding your network.
3. Utilize Network Management Tools:
Leverage network management software for tasks like IP address allocation, subnet management, and network monitoring. Tools like SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor or ManageEngine OpManager can significantly streamline your network management process.
4. Stay Updated:
The networking landscape is constantly evolving, so keeping informed about new technologies and changes in IP addressing standards is crucial. Attend industry events, read relevant publications, and engage in online communities to maintain your expertise.
Frequently Asked Questions
Let’s address some frequently asked questions about subnetting:
Q: What’s the difference between a subnet mask and a default gateway?
A subnet mask determines the network portion of an IP address, while a default gateway is the IP address of the router that connects a subnet to the rest of the network.
Q: Can I change the subnet mask of a network without disrupting traffic?
Changing a subnet mask can disrupt traffic, especially if devices are actively communicating. It’s crucial to understand the implications of such changes and carefully plan the transition to minimize network downtime.
Q: Is subnetting still relevant in the age of IPv6?
Yes, subnetting remains relevant for IPv6, though the need for it may be slightly different. The larger address space in IPv6 allows for greater flexibility, but subnetting concepts are still valuable for network organization and security.
Packet Tracer Subnet An Ipv4 Network
Conclusion
Subnetting is a fundamental aspect of network design and management. By mastering subnetting concepts and utilizing tools like Packet Tracer, you can create efficient, secure, and well-organized IPv4 networks. Remember to start small, document your configurations, and stay updated with evolving network technologies.
Are you interested in learning more about subnet an IPv4 network with Packet Tracer? We would love to hear your thoughts and experiences in the comments below!






